Difference between revisions of "Blynk"
From Digipool-Wiki
(→Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Read Onboard-Button) |
(→Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Read Onboard-Button) |
||
| Line 230: | Line 230: | ||
/* Comment this out to disable prints and save space */ | /* Comment this out to disable prints and save space */ | ||
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial | #define BLYNK_PRINT Serial | ||
| − | |||
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h> | #include <ESP8266WiFi.h> | ||
| Line 243: | Line 242: | ||
char ssid[] = "YourNetworkName"; | char ssid[] = "YourNetworkName"; | ||
char pass[] = "YourPassword"; | char pass[] = "YourPassword"; | ||
| + | |||
| + | #define ButtonPin 0 | ||
int prevState = -1; | int prevState = -1; | ||
| Line 251: | Line 252: | ||
{ | { | ||
// Invert state, since button is "Active LOW" | // Invert state, since button is "Active LOW" | ||
| − | int state = !digitalRead( | + | // int state = !digitalRead(ButtonPin); |
| + | boolean state = !digitalRead(ButtonPin); | ||
// Debounce mechanism | // Debounce mechanism | ||
| Line 261: | Line 263: | ||
if (state != currState) { | if (state != currState) { | ||
currState = state; | currState = state; | ||
| − | Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, state); | + | if (state == 0) { |
| + | Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, 0); | ||
| + | Serial.println("Button Off"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | if (state == 1) { | ||
| + | Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, 1023); | ||
| + | Serial.println("Button On"); | ||
| + | } | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 273: | Line 282: | ||
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass); | Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass); | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | // Make | + | // Make ButtonPin default HIGH, and attach INT to our handler |
| − | pinMode( | + | pinMode(ButtonPin, INPUT_PULLUP); |
} | } | ||
| Line 286: | Line 292: | ||
checkPin(); | checkPin(); | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 16:04, 24 January 2021
Contents
Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Simple-Setup a New-Board
Setup
- Install the Blynk App on your Phone
- Creat an Account and log in
- Scann the QR-Code
- Follow the steps
- If the App is connecting to your Blynk board, open WLAN-Setting and select the boards WLAN by hand
Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Onboard-NeoPixel
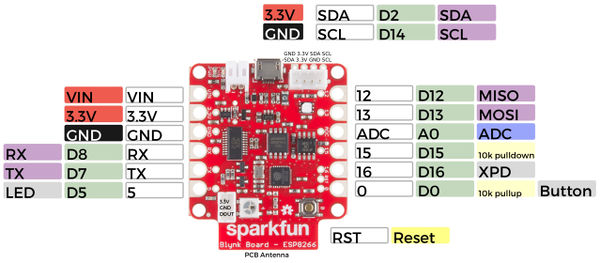
Auf dem Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Board befindet sich eine RGB LED, die sich sehr gut dazu eignet, um zum Beispiel einen aktuellen Zustand anzuzeigen. Diese RGB LED vom Type WS2812 ist mit Pin 4 verdrahtet und kann über die Library Adafruit_NeoPixel.h angesteuert werden.
Onboard-RGB-LED
- Board: Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266
- LED-Type: WS2812
- Library: Adafruit_NeoPixel.h
- Pin: 4
- Example-Code (siehe unten)
- Example-Blynk-App-Settings (siehe unten)
// Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Onboard-NeoPixel Example
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h>
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App.
// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon).
char auth[] = "YourAuthToken";
// Your WiFi credentials.
// Set password to "" for open networks.
char ssid[] = "YourNetworkName";
char pass[] = "YourPassword";
#define PIN 4
int stripR = 0;
int stripG = 0;
int stripB = 0;
int stripL = 0;
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(1, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
BLYNK_WRITE(V1)
{
stripR = param[0].asInt();
stripG = param[1].asInt();
stripB = param[2].asInt();
showRGB();
}
BLYNK_WRITE(V2)
{
stripL = 255 - param.asInt();
showRGB();
}
void showRGB() {
int r = stripR - stripL;
if (r < 0) r = 0;
int g = stripG - stripL;
if (g < 0) g = 0;
int b = stripB - stripL;
if (b < 0) b = 0;
strip.setPixelColor(0, strip.Color(r, g, b));
strip.show();
}
void setup()
{
// Debug console
Serial.begin(9600);
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass);
strip.begin();
strip.show();
}
void loop()
{
Blynk.run();
}
Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Onboard-Temp-Humidity
Auf dem Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Board befindet sich eine Temperatur- und Feuchtigkeitssensor, der sich sehr gut dazu eignet, um zum Beispiel das Raumklima zu erfassen. Diese I2C Sensor vom Type Si7021 ist mit Pin 2 und Pin 14 verdrahtet und kann über die Library SparkFun_Si7021_Breakout_Library.h ausgelesen werden.
Onboard Temperature and Humidity Sensor
- Board: Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266
- Sensor-Type: Si7021
- Library: SparkFun_Si7021_Breakout_Library.h
- Pin: 2 & 14 (werden von der Library automatisch gesetzt)
- Example-Code (siehe unten)
- Example-Blynk-App-Settings (siehe unten)
// Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266_Onboard-TempHumidity_Example
/* Comment this out to disable prints and save space */
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h>
// #include <DHT.h>
#include "SparkFun_Si7021_Breakout_Library.h"
#include <Wire.h>
// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App.
// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon).
char auth[] = "YourAuthToken";
// Your WiFi credentials.
// Set password to "" for open networks.
char ssid[] = "YourNetworkName";
char pass[] = "YourPassword";
float humidity = 0;
float tempf = 0;
float tempc = 0;
//Create Instance of HTU21D or SI7021 temp and humidity sensor and MPL3115A2 barrometric sensor
Weather sensor;
BlynkTimer timer;
// This function sends Arduino's up time every second to Virtual Pin (5).
// In the app, Widget's reading frequency should be set to PUSH. This means
// that you define how often to send data to Blynk App.
void sendSensor()
{
getWeather();
printInfo();
sendValues();
}
void setup()
{
// Debug console
Serial.begin(9600);
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass);
// You can also specify server:
//Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass, "blynk-cloud.com", 80);
//Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass, IPAddress(192,168,1,100), 8080);
//Initialize the I2C sensors and ping them
sensor.begin();
// Setup a function to be called every second
timer.setInterval(1000L, sendSensor);
}
void loop()
{
Blynk.run();
timer.run();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
void getWeather()
{
// Measure Relative Humidity from the HTU21D or Si7021
humidity = sensor.getRH();
// Measure Temperature from the HTU21D or Si7021
// tempf = sensor.getTempF();
tempc = sensor.getTemp();
// Temperature is measured every time RH is requested.
// It is faster, therefore, to read it from previous RH
// measurement with getTemp() instead with readTemp()
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
void printInfo()
{
//This function prints the weather data out to the default Serial Port
Serial.print("Temp:");
Serial.print(tempc);
Serial.print("°C, ");
Serial.print("Humidity:");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.println("%");
}
void sendValues() {
// You can send any value at any time.
// Please don't send more that 10 values per second.
Blynk.virtualWrite(V5, humidity);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V6, tempc);
}
Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Read Onboard-Button
// Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Read Onboard-Button Example
/* Comment this out to disable prints and save space */
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h>
// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App.
// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon).
char auth[] = "YourAuthToken";
// Your WiFi credentials.
// Set password to "" for open networks.
char ssid[] = "YourNetworkName";
char pass[] = "YourPassword";
#define ButtonPin 0
int prevState = -1;
int currState = -1;
long lastChangeTime = 0;
void checkPin()
{
// Invert state, since button is "Active LOW"
// int state = !digitalRead(ButtonPin);
boolean state = !digitalRead(ButtonPin);
// Debounce mechanism
long t = millis();
if (state != prevState) {
lastChangeTime = t;
}
if (t - lastChangeTime > 50) {
if (state != currState) {
currState = state;
if (state == 0) {
Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, 0);
Serial.println("Button Off");
}
if (state == 1) {
Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, 1023);
Serial.println("Button On");
}
}
}
prevState = state;
}
void setup()
{
// Debug console
Serial.begin(9600);
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass);
// Make ButtonPin default HIGH, and attach INT to our handler
pinMode(ButtonPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop()
{
Blynk.run();
checkPin();
}