Blynk
Die Blynk Plattform erlaubt es schnelle und einfach das Arduinos mit dem Handy zu steuern oder Daten von Sensoren auf dem Handy darzustellen.
- Blynk-App — Mit dieser App kann mit fertigen Modulen, wie mit Lego-Bausteinen im Handyumdrehen eine Anwendung erstellt werden. Via Link und QR-Code kann die Anwendung dann veröffentlicht werden
- Blynk-Server — Dieser läuft im Hintergrund des Blynk-Systems und macht den Datenaustausch erst möglich. Gelegentlich fordert die Blynk-App dazu auf, sich an den Server-Kosten zu beteiligen, indem eine sogenannte "Batterie" mit kleinen Beträgen (3 €) aufgeladen werden soll. Blynk bietet auch eine Anleitung zum Aufsetzten eines eigenen Servers.
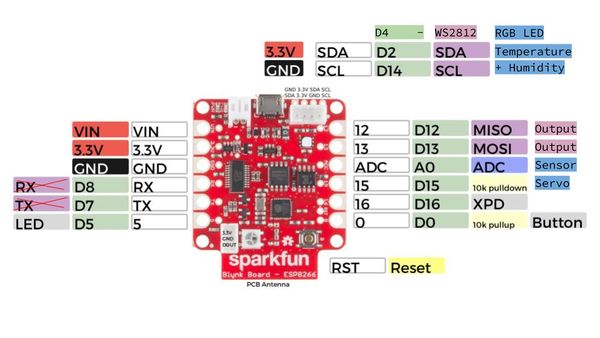
- Sparkfun-Board — Die Blynk-Plattform arbeitet mit einer ganzen Reihe von Arduino-Boards. Eine Liste der kompatiblen Hardware findest Du hier LINK. Das Sparkfun Blynk-ESP8266-Board wurde als kompaktes Bauteil mit WLAN und Akku speziell für Blynk-Projekte konzipiert. Zudem verfügt es über einen Temperatur- und Feuchtigkeitssensor so wie eine RGB-LED und Schnittstellen zu NeoPixel-WS2812-LEDs und I2C-Bauteilen.
Setup
Configuration von Arduino und Blynk
- Installiere das die neuste Arduino-Software
- Schließe das SparkFun-Blynk-Board via USB-Kabel an den Computer an
- Füge das SparkFun Blynk Board zu Arduino hinzu
- Kopiere diese URL: http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json
- Füge die URL unter Arduino / Preferences / Additionel Bords Manager URLs ein
- Wähle unter Tools / Boards / Boardmanager
- Suche nach esp8266
- Installiere esp8266 — by ESP8266 Community
- Jetzt kannst Du unter Tools / Board / ESP8266 Boards / SparkFun Blynk Board anwählen
- Wähle unter Tools / Port / usbserial-.... an
- Falls unter Windows kein Port verfügbar ist, muss der FTDI-Treiber installiert werden — FTDI-Treiber-Download
- Danauch die Arduino-Software neu starten (evt. das Windows neu starten)
- Lade die Libraries aus dieser ZIP-Datei herunter
- Kopiere die Lybrarie in den Arduino-Libraries-Folder unter Documents / Arduino / Libraries
- [Arduino Big-Sur (Mac OS 11.01) Bug Workaround]
- Installiere die Blynk-App auf deinem Smartphone
- Eröffne dein eigenes Blynk-Konto
Benutzung
- Starte am Handy ein Projekt, indem Du in der Blynk-App ein neues Projekt erstellst
- Dir wird automatisch eine E-Mail mit dem App-Token zugeschickt
- Öffne die E-Mail am Computer und kopiere den Token
- Öffne einen Beispiel-Code in der Arduino-Software
- Füge in den Code den Token ein — "YourAuthToken"
- Füge in den Code die Zugangsdaten zu deinem WLAN ein "YourNetworkName" und "YourPassword"
- Lade den Code auf das Blynk-Board
- Nach dem automatischen Neustart des Boards kann die Blynk-App gestartet werden und sollte nun in Verbindung mit dem Board funktionieren
Examples für die Onboard-Bauteile
Das SparkFun-Blynk-Board ist bereits mit einigen interessanten Bauteilen wie Sensoren und LEDs bestückt, die leider kaum dokumentiert sind. (Der Blynk-Example-Code-Builder ist leider nicht mehr aktuell.) Daher demonstrieren diese Beispiele, wie die Onboard-Bauteile angesteuert werden können.
Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Onboard-LED
Auf dem Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Board befindet sich ein LED, der sich gut dazu eignet, um zum Beispiel den aktuellen Zustand eines Ausgangs darzustellen. Diese LED ist mit Pin 5 verdrahtet und kann auch darüber in der App angesteuert werden. Da die digitealen Pins (GP5) von der Blynk-Library automatisch geschlatet werden ist kein zusätzlicher Code nötig.
Onboard-LED
- Board: Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266
- Onboard-LED (eine ganz normale LED)
- Pin: 5
- Example-Blynk-App-Settings (siehe unten)
- Example-Code (siehe unten)
// Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Onboard-LED Example
/* Comment this out to disable prints and save space */
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h>
// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App.
// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon).
char auth[] = "YourAuthToken";
// Your WiFi credentials.
// Set password to "" for open networks.
char ssid[] = "YourNetworkName";
char pass[] = "YourPassword";
void setup()
{
// Debug console
Serial.begin(9600);
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass);
}
void loop()
{
Blynk.run();
// You can inject your own code or combine it with other sketches.
// Check other examples on how to communicate with Blynk. Remember
// to avoid delay() function!
}
Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Read Onboard-Button
Auf dem Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Board befindet sich ein Taster, der sich gut dazu eignet, um zum Beispiel den aktuellen Zustand einer Tür (Reed-Schalter) in der App sichtbar zu machen. Dieser Taster ist mit Pin 0 verdrahtet und kann ober einen virtuellen Pin gelesen werden.
Onboard-RGB-LED
- Board: Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266
- Onboard-Taster an Pin — kann auch über einen externen Taster zischen Pin 0 und GND geschaltet werden
- Example-Code (siehe unten)
- Example-Blynk-App-Settings (siehe unten)
// Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Read Onboard-Button Example
/* Comment this out to disable prints and save space */
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h>
// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App.
// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon).
char auth[] = "YourAuthToken";
// Your WiFi credentials.
// Set password to "" for open networks.
char ssid[] = "YourNetworkName";
char pass[] = "YourPassword";
#define ButtonPin 0
int prevState = -1;
int currState = -1;
long lastChangeTime = 0;
void checkPin()
{
// Invert state, since button is "Active LOW"
// int state = !digitalRead(ButtonPin);
boolean state = !digitalRead(ButtonPin);
// Debounce mechanism
long t = millis();
if (state != prevState) {
lastChangeTime = t;
}
if (t - lastChangeTime > 50) {
if (state != currState) {
currState = state;
if (state == 0) {
Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, 0);
Serial.println("Button Off");
}
if (state == 1) {
Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, 1023);
Serial.println("Button On");
}
}
}
prevState = state;
}
void setup()
{
// Debug console
Serial.begin(9600);
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass);
// Make ButtonPin default HIGH, and attach INT to our handler
pinMode(ButtonPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop()
{
Blynk.run();
checkPin();
}
Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Onboard-NeoPixel
Auf dem Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Board befindet sich eine RGB LED, die sich sehr gut dazu eignet, um zum Beispiel einen aktuellen Zustand anzuzeigen. Diese RGB LED vom Type WS2812 ist mit Pin 4 verdrahtet und kann über die Library Adafruit_NeoPixel.h angesteuert werden.
Onboard-RGB-LED
- Board: Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266
- LED-Type: WS2812
- Library: Adafruit_NeoPixel.h
- Pin: 4
- Example-Code (siehe unten)
- Example-Blynk-App-Settings (siehe unten)
// Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Onboard-NeoPixel Example
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h>
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App.
// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon).
char auth[] = "YourAuthToken";
// Your WiFi credentials.
// Set password to "" for open networks.
char ssid[] = "YourNetworkName";
char pass[] = "YourPassword";
#define PIN 4
int stripR = 0;
int stripG = 0;
int stripB = 0;
int stripL = 0;
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(1, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
BLYNK_WRITE(V1)
{
stripR = param[0].asInt();
stripG = param[1].asInt();
stripB = param[2].asInt();
showRGB();
}
BLYNK_WRITE(V2)
{
stripL = 255 - param.asInt();
showRGB();
}
void showRGB() {
int r = stripR - stripL;
if (r < 0) r = 0;
int g = stripG - stripL;
if (g < 0) g = 0;
int b = stripB - stripL;
if (b < 0) b = 0;
strip.setPixelColor(0, strip.Color(r, g, b));
strip.show();
}
void setup()
{
// Debug console
Serial.begin(9600);
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass);
strip.begin();
strip.show();
}
void loop()
{
Blynk.run();
}
Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Onboard-Temp-Humidity Senor
Auf dem Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266 Board befindet sich eine Temperatur- und Feuchtigkeitssensor, der sich sehr gut dazu eignet, um zum Beispiel das Raumklima zu erfassen. Diese I2C Sensor vom Type Si7021 ist mit Pin 2 und Pin 14 verdrahtet und kann über die Library SparkFun_Si7021_Breakout_Library.h ausgelesen werden.
Onboard Temperature and Humidity Sensor
- Board: Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266
- Sensor-Type: Si7021
- Library: SparkFun_Si7021_Breakout_Library.h
- Pin: 2 & 14 (werden von der Library automatisch gesetzt)
- Example-Code (siehe unten)
- Example-Blynk-App-Settings (siehe unten)
// Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266_Onboard-TempHumidity_Example
/* Comment this out to disable prints and save space */
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h>
// #include <DHT.h>
#include "SparkFun_Si7021_Breakout_Library.h"
#include <Wire.h>
// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App.
// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon).
char auth[] = "YourAuthToken";
// Your WiFi credentials.
// Set password to "" for open networks.
char ssid[] = "YourNetworkName";
char pass[] = "YourPassword";
float humidity = 0;
float tempf = 0;
float tempc = 0;
//Create Instance of HTU21D or SI7021 temp and humidity sensor and MPL3115A2 barrometric sensor
Weather sensor;
BlynkTimer timer;
// This function sends Arduino's up time every second to Virtual Pin (5).
// In the app, Widget's reading frequency should be set to PUSH. This means
// that you define how often to send data to Blynk App.
void sendSensor()
{
getWeather();
printInfo();
sendValues();
}
void setup()
{
// Debug console
Serial.begin(9600);
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass);
// You can also specify server:
//Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass, "blynk-cloud.com", 80);
//Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass, IPAddress(192,168,1,100), 8080);
//Initialize the I2C sensors and ping them
sensor.begin();
// Setup a function to be called every second
timer.setInterval(1000L, sendSensor);
}
void loop()
{
Blynk.run();
timer.run();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
void getWeather()
{
// Measure Relative Humidity from the HTU21D or Si7021
humidity = sensor.getRH();
// Measure Temperature from the HTU21D or Si7021
// tempf = sensor.getTempF();
tempc = sensor.getTemp();
// Temperature is measured every time RH is requested.
// It is faster, therefore, to read it from previous RH
// measurement with getTemp() instead with readTemp()
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
void printInfo()
{
//This function prints the weather data out to the default Serial Port
Serial.print("Temp:");
Serial.print(tempc);
Serial.print("°C, ");
Serial.print("Humidity:");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.println("%");
}
void sendValues() {
// You can send any value at any time.
// Please don't send more that 10 values per second.
Blynk.virtualWrite(V5, humidity);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V6, tempc);
}
Besonderheiten des Sparkfun-Blynk-ESP8266
BlynkTimer
DeepSleep
low-power operation DeepSleep
Blynk + P5*JS